Delving into Electric mobility trends in Asia and Europe, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative. The current state of electric mobility adoption, government policies, and cultural influences in these regions are explored to provide a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
As we navigate through the landscape of electric mobility trends in Asia and Europe, it becomes evident that the interplay between technological innovations, infrastructure development, and market trends shapes the future of transportation in these regions.
Electric Mobility Trends in Asia and Europe
Electric mobility is gaining traction in both Asia and Europe, but the current state of adoption differs significantly between the two regions. While Europe leads the way in electric vehicle (EV) sales and infrastructure development, Asia is quickly catching up, driven by countries like China and Japan.
Government Policies
In Europe, governments have been proactive in promoting electric mobility through a combination of incentives, subsidies, and strict emission regulations. Countries like Norway and the Netherlands have implemented policies to phase out internal combustion engine vehicles in the coming years.
On the other hand, Asian countries like China have set ambitious targets for EV sales and production, encouraging investment in charging infrastructure and research and development.
Cultural Factors
Cultural factors play a significant role in the acceptance of electric vehicles in both Asia and Europe. In Europe, the emphasis on environmental sustainability and the presence of eco-conscious consumers have driven the demand for EVs. In contrast, in Asia, factors like air pollution concerns in densely populated cities and government support for clean energy technologies have fueled the growth of electric mobility.
Infrastructure Development
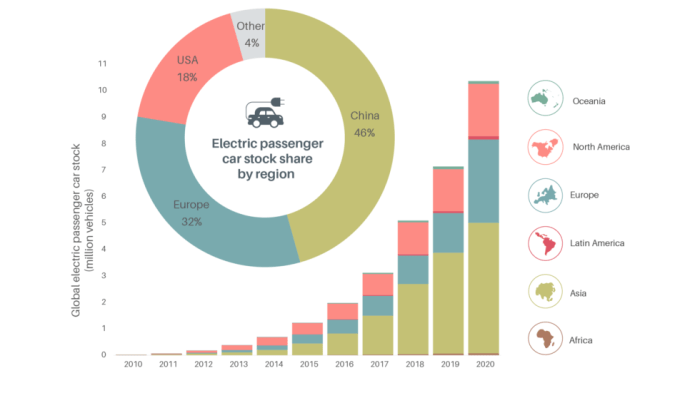
Electric mobility in Asia and Europe faces significant challenges in infrastructure development, particularly in the establishment of charging stations. The availability of a robust charging infrastructure is crucial for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles and the transition towards sustainable transportation systems.
Investment in Charging Stations
- Asian countries such as China and Japan have made substantial investments in charging infrastructure to support the growing number of electric vehicles on their roads. China, in particular, has been leading the way in terms of the number of charging stations installed.
- In Europe, countries like Norway and the Netherlands have also shown a strong commitment to developing charging infrastructure. Norway, for instance, has one of the highest rates of electric vehicle adoption in the world, supported by a well-established network of charging stations.
- Overall, both regions are making progress in expanding their charging infrastructure, with government incentives and regulations playing a significant role in driving investment in this area.
Public-Private Partnerships
- Public-private partnerships have emerged as a key strategy for developing charging infrastructure in both Asia and Europe. By leveraging the resources and expertise of both sectors, governments can accelerate the deployment of charging stations and overcome financial barriers.
- In Asia, collaborations between government agencies, electric utilities, and private companies have been instrumental in expanding the charging network. These partnerships help distribute the costs of infrastructure development and ensure a more efficient rollout of charging stations.
- In Europe, public-private partnerships have also been successful in driving investment in charging infrastructure. Companies specializing in electric vehicle charging solutions have partnered with governments to establish a comprehensive network of charging stations across the continent.
Technological Innovations
Electric mobility in Asia and Europe is being driven by a wave of technological advancements that are shaping the future of transportation. From AI and IoT integration to breakthroughs in battery technology, these innovations are revolutionizing the efficiency and performance of electric vehicles in both regions.
Role of AI and IoT
AI and IoT technologies are playing a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency of electric vehicles in Asia and Europe. By leveraging artificial intelligence for predictive maintenance and optimizing energy consumption, EVs are becoming more reliable and cost-effective. IoT connectivity allows for real-time data monitoring and analysis, enabling smarter charging solutions and improving overall vehicle performance.
Emerging Trends in Battery Technology
The rapid development of battery technology is a game-changer for electric vehicles, with Asia and Europe at the forefront of innovation. Lithium-ion batteries continue to dominate the market, but advancements in solid-state batteries and fast-charging solutions are on the rise.
These new technologies promise longer driving ranges, shorter charging times, and increased overall durability, making electric vehicles more practical and appealing to consumers.
Market Trends
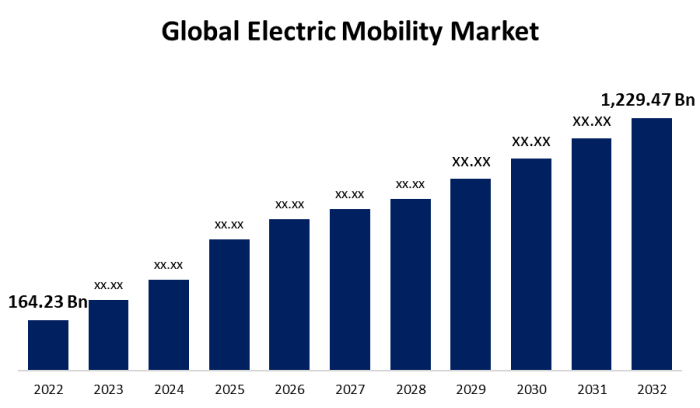
Electric vehicles are gaining popularity worldwide, but the market share of EVs in Asia and Europe varies significantly. In Europe, EVs have a higher market share compared to Asia, with countries like Norway leading the way in adoption rates. On the other hand, Asia is seeing rapid growth in EV sales, especially in China and Japan.
Market Share of Electric Vehicles
In Europe, countries like Norway, the Netherlands, and Sweden have a higher market share of electric vehicles compared to other European nations. Norway, in particular, has set ambitious targets to phase out traditional internal combustion engine vehicles in favor of EVs.
On the other hand, China dominates the Asian market for electric vehicles, followed closely by Japan and South Korea. These countries have implemented various incentives and subsidies to encourage EV adoption.
Consumer Preferences for Electric Vehicles
Consumer preferences for electric vehicles vary across different countries within Asia and Europe. In Europe, consumers are more environmentally conscious and tend to prefer EVs for their lower carbon emissions. In contrast, Asian consumers often choose EVs for their cost-effectiveness and government incentives.
Countries like China have a growing middle class that is increasingly opting for electric vehicles as a status symbol.
Pricing Trends and Affordability
The pricing trends of electric vehicles have been gradually decreasing, making them more affordable for the masses. In Europe, governments offer subsidies and tax incentives to make EVs more accessible to consumers. Similarly, Asian countries like China provide financial incentives and tax breaks to promote the adoption of electric vehicles.
As technology advances and economies of scale improve, the cost of EVs is expected to further decrease, making them a more viable option for consumers worldwide.
Final Summary
In conclusion, the dynamic nature of electric mobility trends in Asia and Europe highlights the potential for significant growth and evolution in the coming years. By examining the various factors influencing the adoption of electric vehicles, we gain valuable insights into the sustainable future of transportation.
Helpful Answers
What are the key differences in government policies promoting electric mobility in Asia and Europe?
In Asia, some countries offer significant incentives and subsidies for electric vehicles, while in Europe, there is a stronger focus on stringent emissions regulations and targets.
How do cultural factors impact the acceptance of electric vehicles in Asia and Europe?
Cultural perceptions of technology, environmental awareness, and economic factors play a significant role in influencing the adoption of electric vehicles in both regions.
What are the emerging trends in battery technology and how do they impact electric vehicle performance?
Advancements in battery technology, such as solid-state batteries and fast-charging capabilities, are enhancing the range and efficiency of electric vehicles in Asia and Europe.










